While the emergence of ChatGPT has created considerable consternation among faculty who fear students will use it to write their assignments, the positive side is that it provides a powerful tool for faculty to use in developing course content. ChatGPT can assist in all areas of course development, from overall course structure to assignments, resources, and rubrics. It can even focus on different instructional strategies, such as experiential learning, active learning, or blended learning. The trick is to ask it for the most structure first, then keep narrowing down the focus with follow-up questions that bore down into specific areas. Here is an example of that process.
Course design
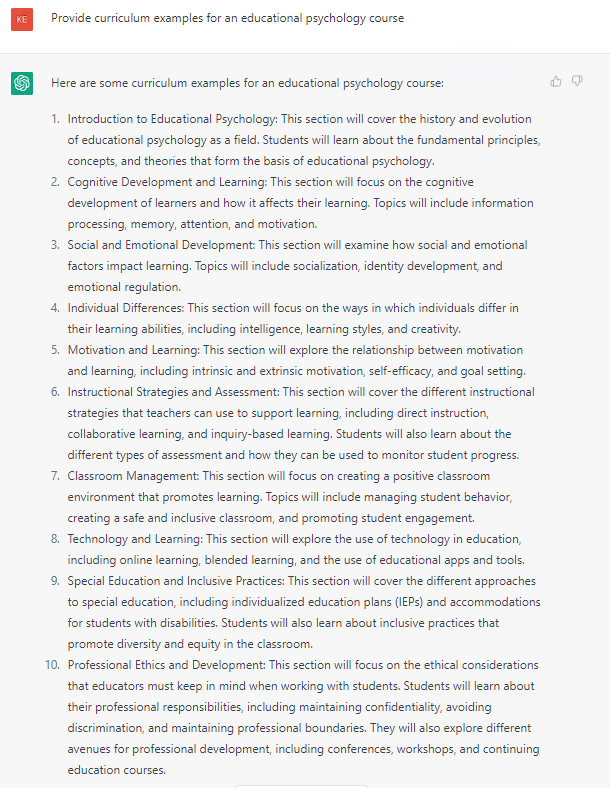
Imagine you are tasked with developing a new educational psychology course. You can start with the simple prompt, “Provide curriculum examples for an educational psychology course.” As the screenshot below illustrates, the AI system provides a list of topics that fit the course. Althought the list is not exhaustive, it is a good start for course development, and you can ask further questions to broaden the list.
Specific lesson development
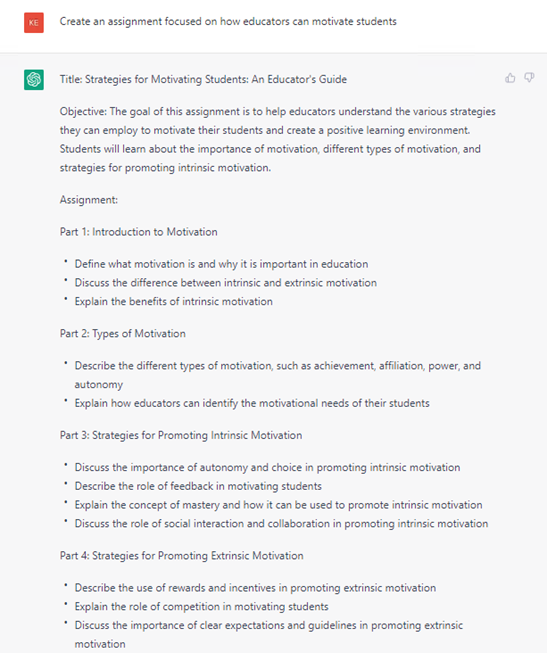
Having developed the general course structure, you can then flesh out the particular topics. For example, educational psychology courses are often integrated into teacher education programs. One focus of these programs is student motivation, and thus we asked ChatGPT to “create an assignment focused on how educators can motivate students.” As illustrated below, the output included a lesson title, an objective, assignment directions, and an assessment.

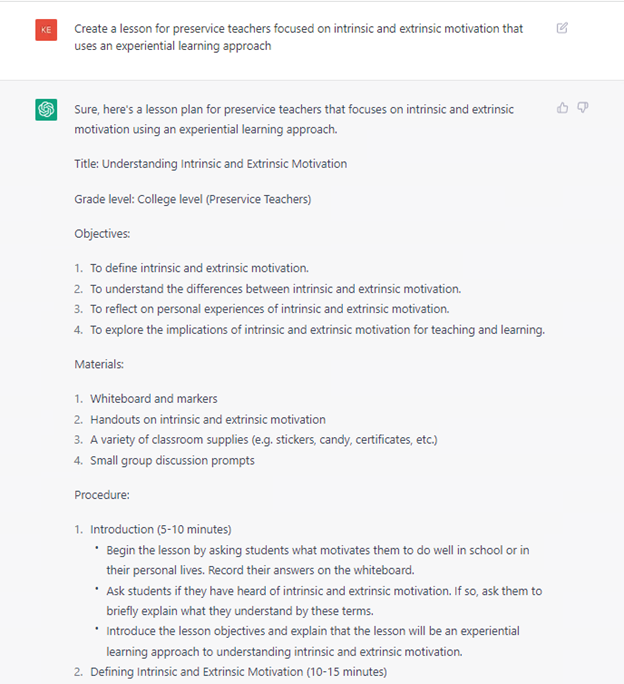
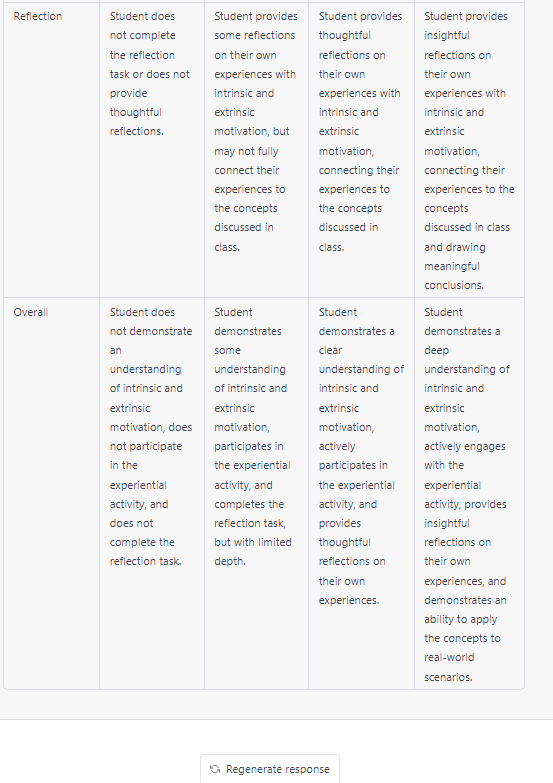
This is good start, but imagine that we want to dig deeper to include the impact of intrinsic and extrinsic motivational factors as well as focus on serving preservice teachers. Thus, we can ask ChatGPT to “create a lesson for preservice teachers focused on intrinsic and extrinsic motivation that uses an experiential learning approach.”
In the below output, the objective of the lesson places more emphasis on intrinsic than extrinsic motivation. Additionally, the inclusion of experiential learning activities would benefit learners in providing direct experience and focused reflection to increase learners’ knowledge of this subject. By completing experiential learning activities, students engage in active learning that enhances their levels of understanding, broadens their perspectives, and helps them develop positive professional practices and skills.

You can further question the AI platform to “provide essentail questions for this lesson.” These types of questions provide faculty overarching questions to guide their lessons to ensure students engage in critical thinking and engage with their existing knowledge base. Faculty can use these questions to set the stage for learning, engaging learners, and incorporating opportunities for real-world connections. Continuing with the motivation lesson plan, ChatGPT provided the below output for essential questions for the course.

Now you might want to generate some potential responses to these questions. For instance, you might ask it to “provide three possible ways for students to demonstrate understanding for question #2.” This level of detail informs you of potential ways to structure student reponses and how they can direct learning.

Rubric creation
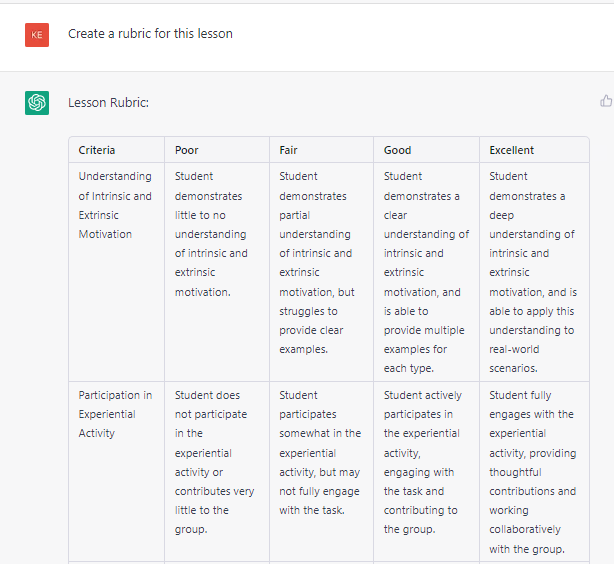
When further prompted, the system also created a rubric to align with the assignment. You can adjust the point values for each criterion or further expand on the recommended criteria to ensure alignment with the assignment components. Regardless of how you modify the rubric content, the ChatGPT output can reduce valuable time and effort required to locate rubrics or to create new rubric tools. Nevertheless, to ensure that appropriate rubrics are created by AI tools, be sure to review rubric content for accuracy and assignment alignment.
When creating course rubrics via AI, a first step is to define the learning outcomes and criteria for the assignment or assessment. This approach involves specifying what students should be able to do, know, or demonstrate and the criteria or standards for evaluating their work. Once you have defined the learning outcomes and criteria, you can input the data into an AI tool. The AI tool will generate a preliminary rubric based on the input data. As with all AI-generated content, you should review this rubric to ensure that it accurately reflects the learning outcomes and criteria. Copy the generated content into the assignment rubric and modify as appropriate for alignment.
ChatGPT considerations
Faculty can use ChatGPT as a starting point for curriculum development by using its vast knowledge base and language generation capabilities. Even if you need to modify the output provided by the platform, you will most likely experience a reduction in your curriculum development efforts. You should, however, prudently review AI-generated language for accuracy and alignment of curriculum goals. For instance, AI platforms can share curriculum enhancements that include multimedia elements such as videos, images, interactive activities, and simulations. But when reviewing these suggestions, you should consider accessibility, usability, alignment to curriculum, and cost—important factors that the AI platform may not account for. Additional limitations include disciplinary blind spots that you should examine to ensure that curriculum reflects contextual knowledge and judgment in ways that are not yet possible for AI language models. Chatbots are also limited in their knowledge of current events and often cannot produce examples from recent years. Using current events in curriculum is valuable for creating student engagement and providing examples that connect learning to real-world issues and events.
ChatGPT can generate content quickly and efficiently, but it is important to add your own perspectives and insights to ensure that the curriculum reflects your teaching style and approach. It is also important to consider issues such as bias and accountability. Finally, make sure that the use of ChatGPT aligns with institutional policies and regulations and that it complies with the institution’s policies on intellectual property and academic dishonesty.
The tool is continuously learning and improving (Gleason, 2022), which leads to more detailed, accurate, and sophisticated results as time goes on. Embracing what AI offers can result in a more meaningful and engaging teaching and learning experience.
Reference
Gleason, N. (2022, December 9). ChatGPT and the rise of AI writers: How should higher education respond? Times Higher Education. https://www.timeshighereducation.com/campus/chatgpt-and-rise-ai-writers-how-should-higher-education-respond
Kelly M. Torres, PhD, is the department chair and Aubrey Statti, EdD, is a core faculty member of the educational psychology and technology program at The Chicago School of Professional Psychology.






